THE NEW LAND GRAIN CORRIDOR
The most profitable route for Siberian grain export
NEW LAND GRAIN CORRIDOR GROUP OF COMPANIES
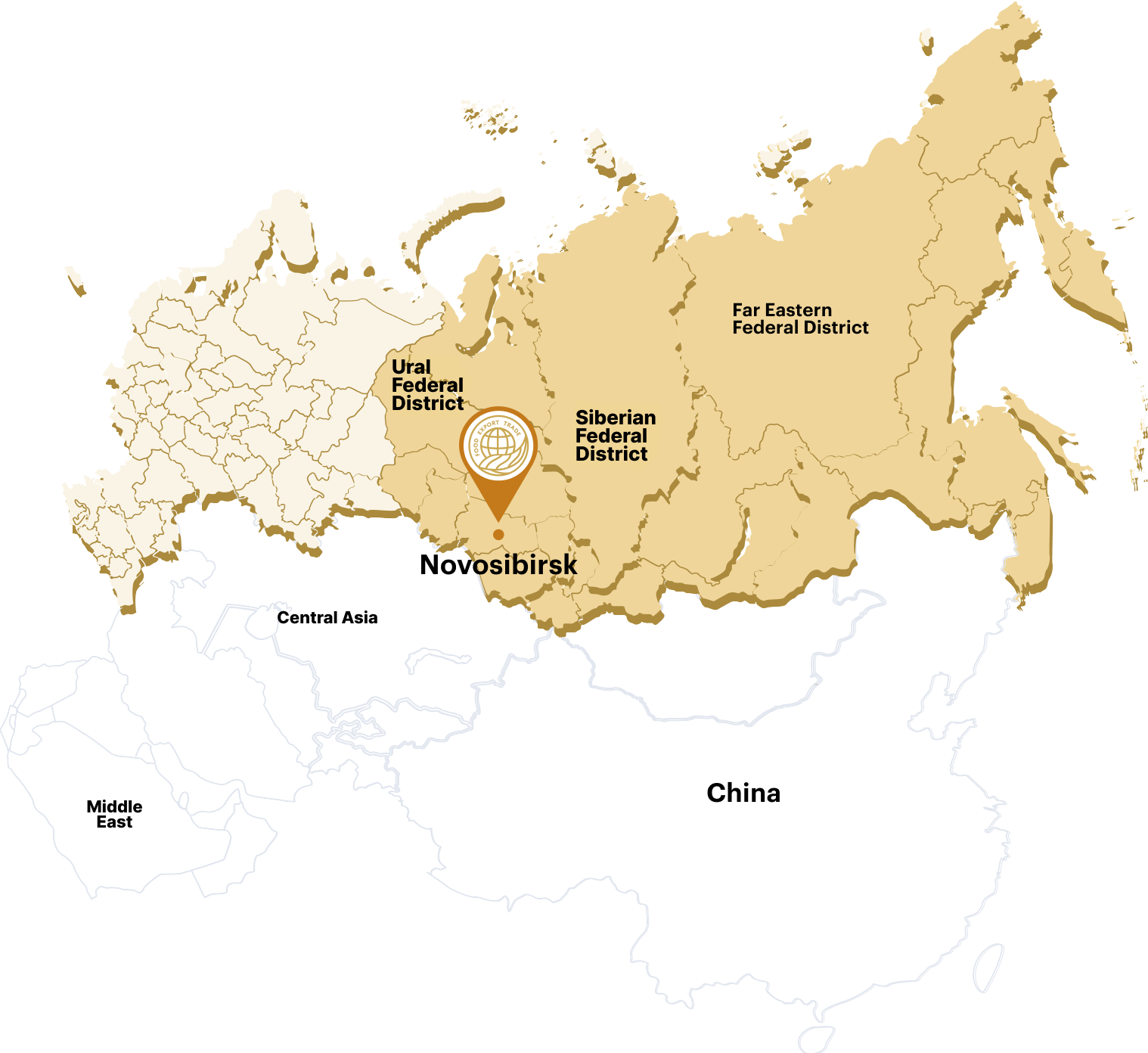
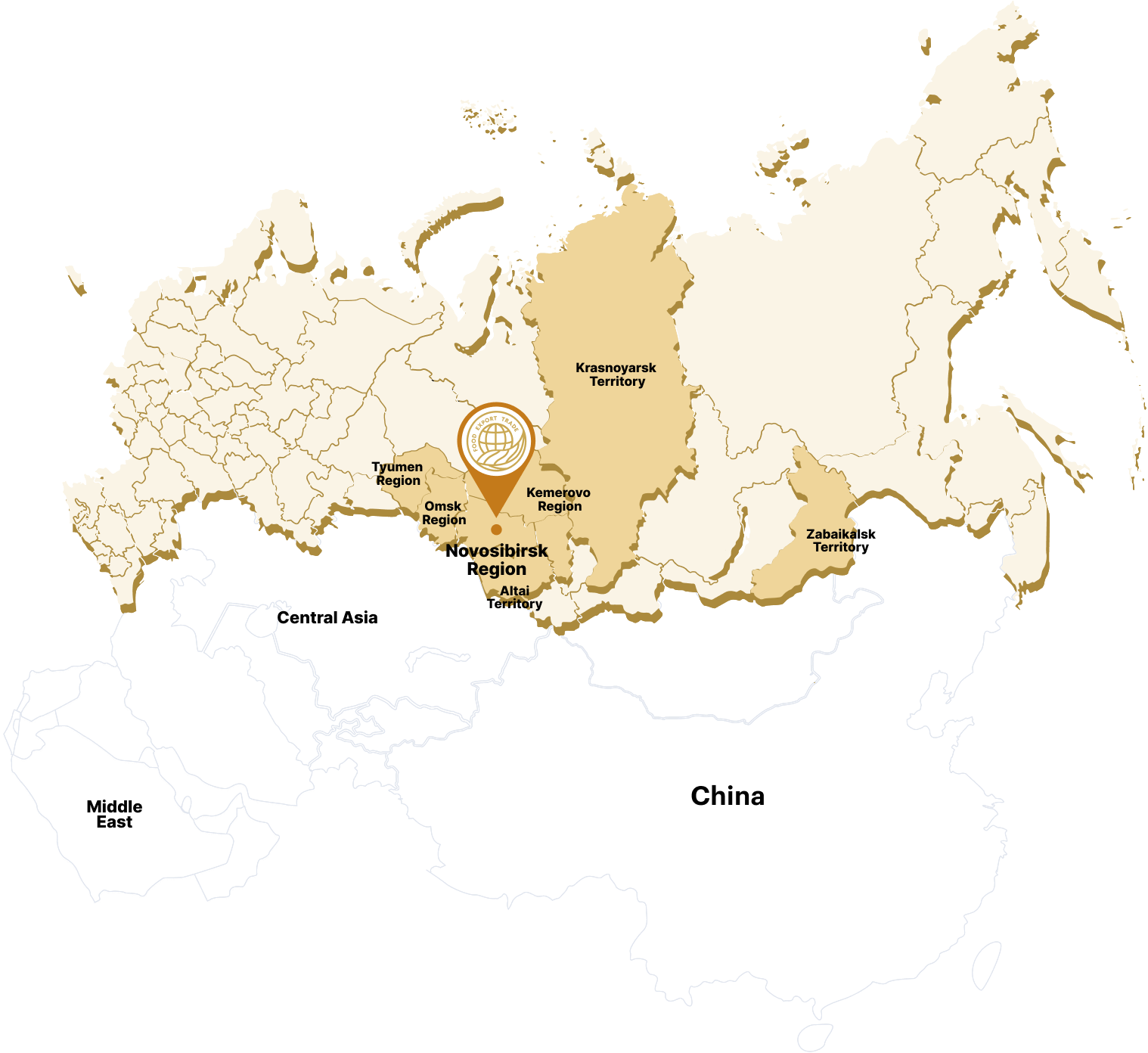
An export-oriented holding structure exporting grains, grain legumes and oilseeds from Ural, Siberia and the Far East to China, Central Asia and the Middle East
How things work




Key Advantages
 Wide range of the state support measures" />
Wide range of the state support measures" />
At the international, federal and regional levels
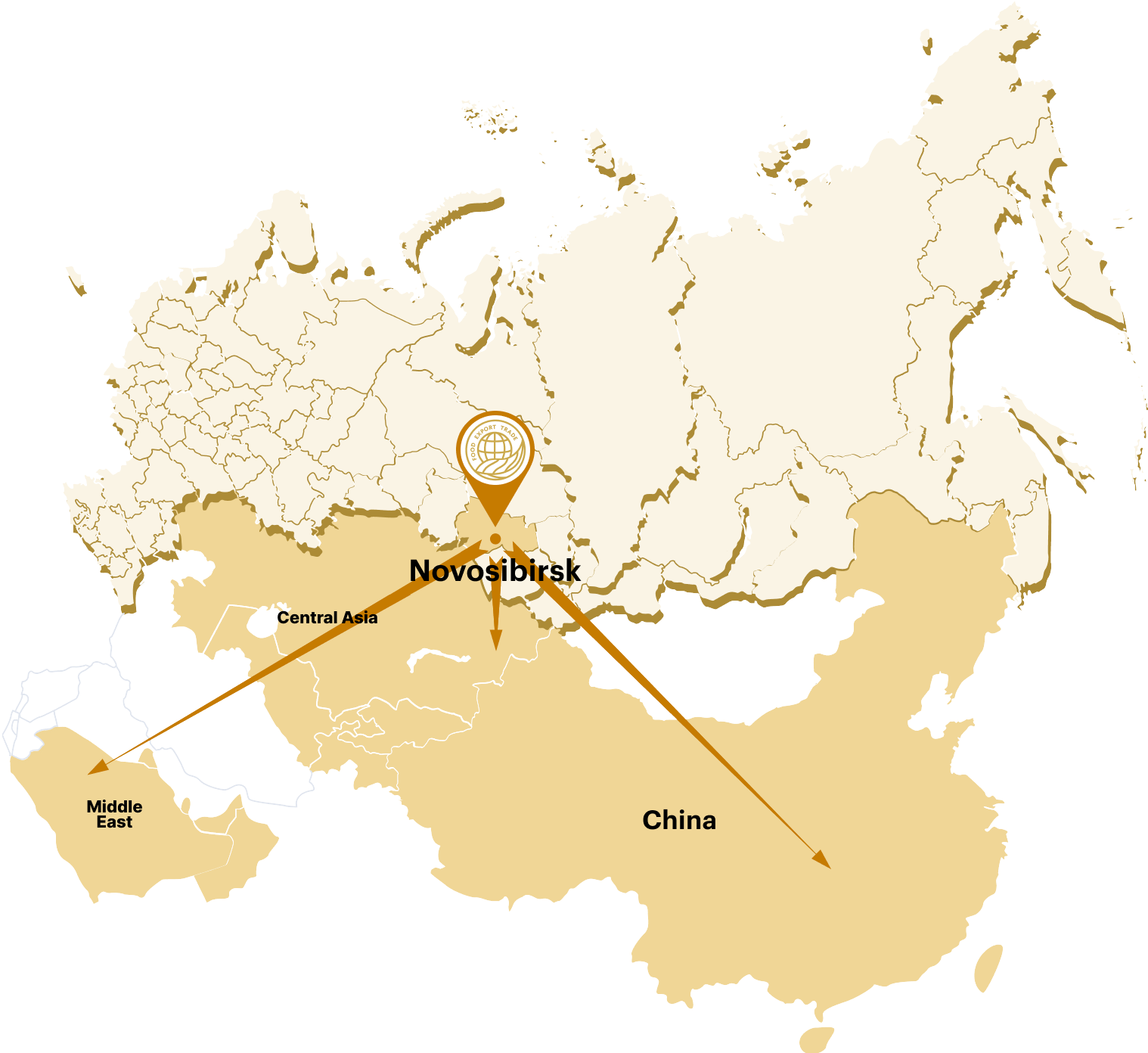
 The largest global markets" />
The largest global markets" />
Only China imports over 100 million tons of grains, grain legumes and oilseeds annually
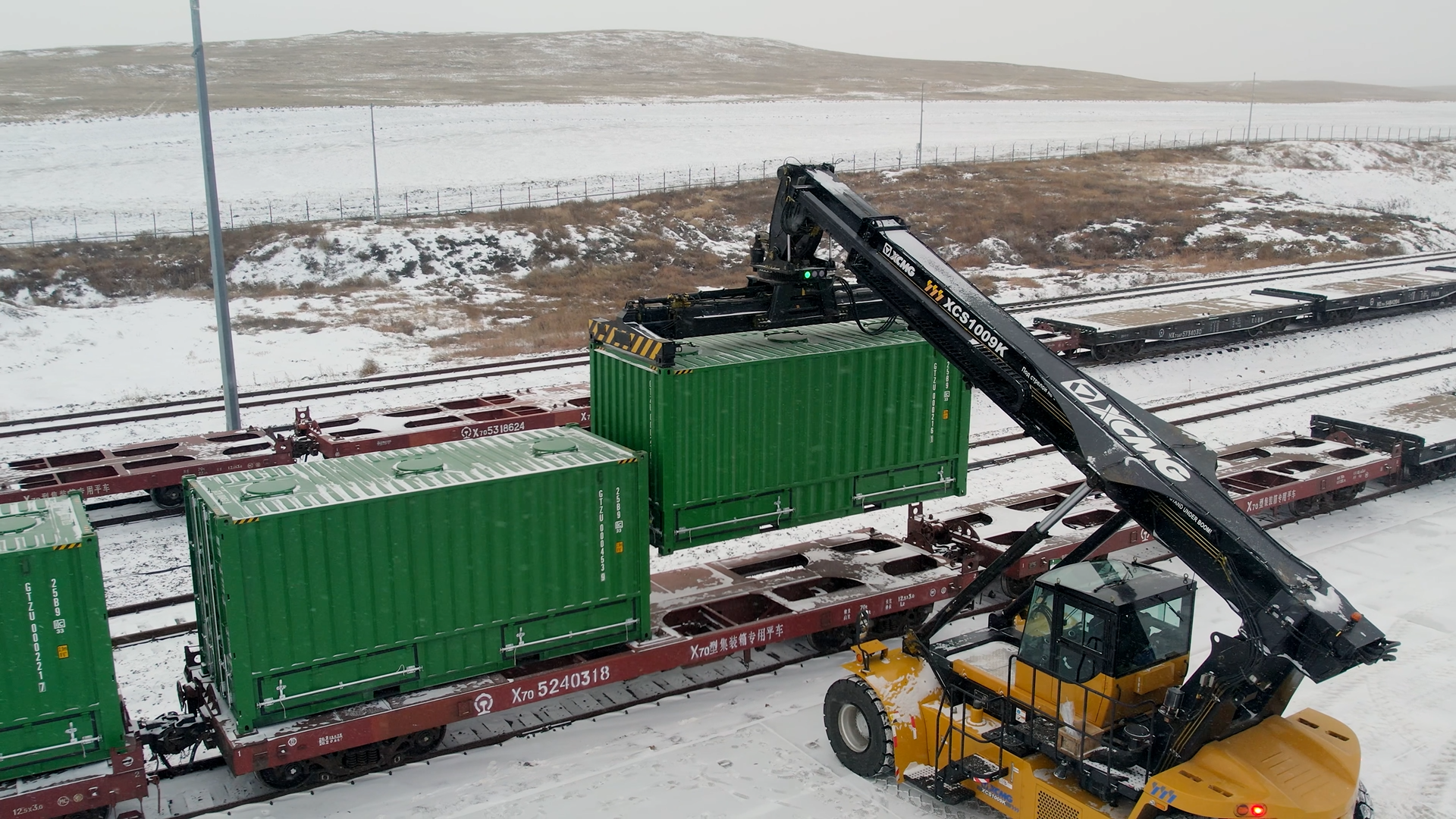
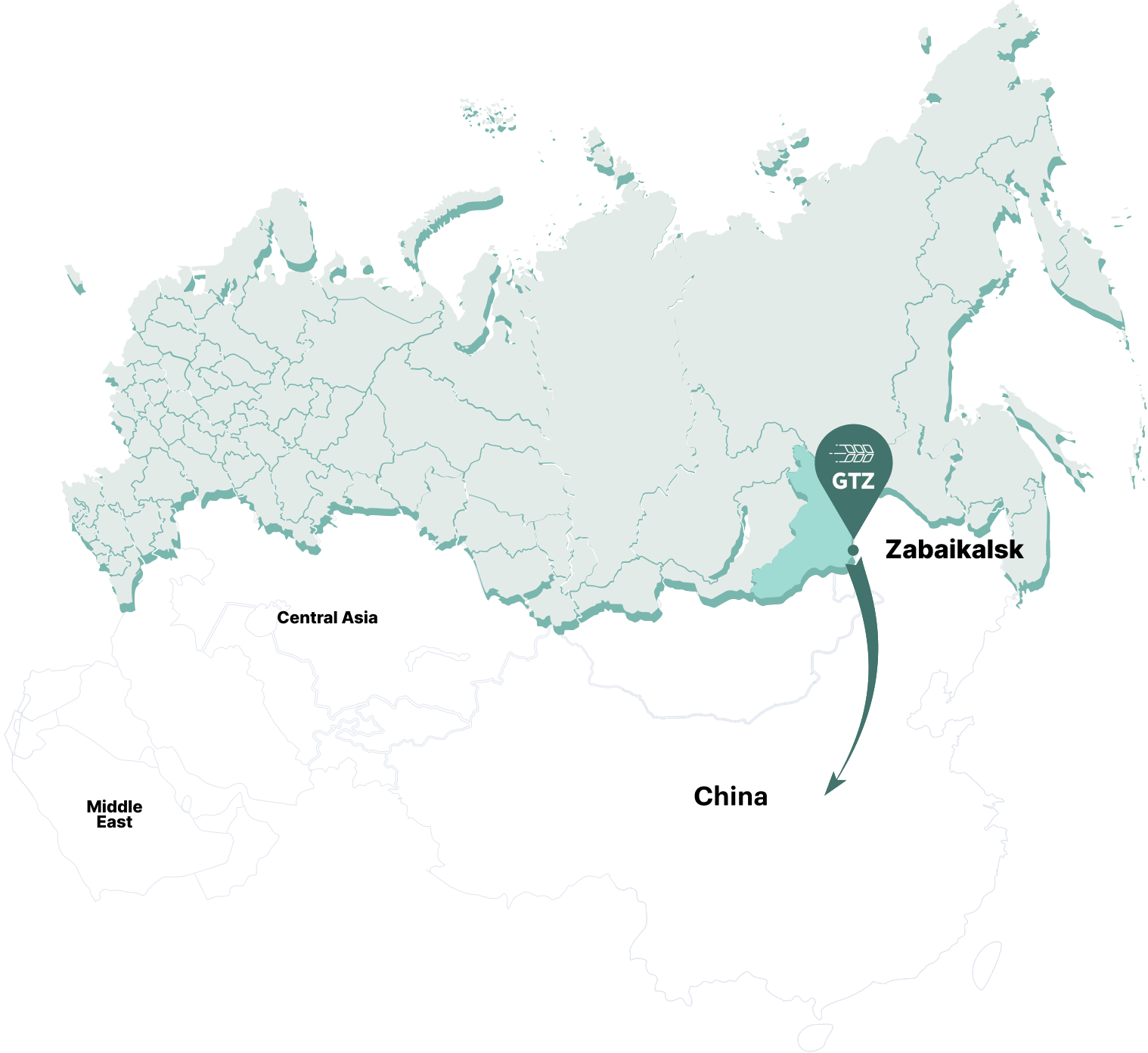
 Unique process approach to grain transshipment" />
Unique process approach to grain transshipment" />
Through connection to 1520 mm and 1435 mm gauge wheel tracks
 Available raw materials base" />
Available raw materials base" />
Development of contract manufacturing on the basis of long-term contracts with manufacturers
 Short logistics leg" />
Short logistics leg" />
The most profitable route for grain deliveries to China which reduces the logistic costs by almost 35% (due to no transshipment at port)
Transshipped Crops
Given the production capacities and the export potential of the regions in the Siberian Federal District, the Ural Federal District and the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the demand of China and Central Asia for grains and oilseeds, the target crops for the contract manufacturing include soybeans, rapeseed, barley, flax, wheat, corn, sunflower seed, and oat.


SOYBEANS
Each year in Russia, including Siberia, the production of soybeans (non-GMO soybeans) increases steadily. Our company actively promotes soybean production and organizes deliveries to the key demand markets, including the world’s largest soybean consumption market — China.
.jpg)

RAPESEED
Production of rapeseed in Siberia is gaining momentum: the areas under crop and yield are increasing. High profitability and potential of export to the Asian countries are the reasons why the crop is so popular.


BARLEY
Barley is the most mass-produced and supplied cereal crop after wheat. Two-row barley is the so-called malting barley. Two-row barley is in demand by the brewing industry, which is growing rapidly, especially in the Asia-Pacific region.


FLAX
Flax farming is again on the cutting edge. Low effective temperatures are enough for flax to grow. All this allows to seed and effectively farm flax in Eastern Siberia.
.jpg)

WHEAT
Durum wheat is used for pasta production. It likes a relatively dry climate, so, given the climatic conditions of southeastern Siberia, it is produced here in excellent quality.
.jpg)

CORN
Today corn is produced all over Russia, where the climate allows it, including the geography of the Great Siberia. An important feature of Russian corn is the ban on GMO varieties.
.jpg)

SUNFLOWER SEED
Traditionally, sunflower seeds are grown in the South and Center of Russia; in Siberia, Altai is famous for the production of this crop. The geography of production is expanding because of the development of new crop varieties and climate change in the direction of warming.










